Cryptocurrency has taken the financial world by storm, fundamentally reshaping how people think about money, security, and digital ownership. As more individuals and businesses embrace decentralized finance, understanding the inner workings of cryptocurrency transactions becomes critical. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or a beginner stepping into this exciting space, grasping how crypto transactions operate how they are sent, received, and validated will empower you to navigate the digital economy with confidence.
At the heart of any cryptocurrency network lies the concept of a transaction. It’s more than just sending digital coins from one address to another; it’s about leveraging a decentralized system that relies on cryptographic proof rather than third-party trust. Cryptocurrency transactions play a crucial role in enabling trustless exchanges, ensuring transparency, and maintaining the integrity of the entire blockchain ecosystem.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk through the complete lifecycle of a cryptocurrency transaction. From initiation to validation and confirmation, you’ll learn how value flows across decentralized networks and what happens behind the scenes when you click “send.” Let’s delve deep into the world of cryptocurrency transactions and unravel the mechanics behind sending and receiving crypto.
The Foundation of Cryptocurrency Transactions
To understand how cryptocurrency transactions work, it’s important to first recognize the decentralized nature of blockchain technology. Unlike traditional banking systems, where transactions are mediated by financial institutions, cryptocurrencies operate on peer-to-peer networks. These systems allow individuals to transfer digital assets directly to one another, often across international borders, without the need for intermediaries.
When a cryptocurrency transaction is made, it doesn’t rely on a central authority to verify or authorize the payment. Instead, the network relies on a combination of cryptographic algorithms, public ledgers, and consensus mechanisms to ensure every transaction is valid and secure. Every user involved has a public address, typically derived from their wallet, which acts as their identity on the blockchain.
At the core of these systems is a public ledger known as the blockchain. This ledger records every transaction that occurs on the network, ensuring transparency and accountability. Once a transaction is confirmed and added to the blockchain, it becomes immutable—meaning it cannot be altered or deleted. This is one of the major reasons cryptocurrency transactions are considered secure and trustworthy.
Initiating a Cryptocurrency Transaction
Sending a cryptocurrency transaction usually begins with a wallet. Whether you’re using a mobile app, desktop software, or a hardware device, your crypto wallet plays a central role in managing your digital funds. Every wallet contains a pair of cryptographic keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is like your bank account number, while the private key is akin to your password.
When you decide to send cryptocurrency to another person, you’ll need their public address. This address is where the digital assets will be delivered. You input the recipient’s address, specify the amount, and authorize the transaction using your private key. This digital signature ensures that only the rightful owner of the wallet can initiate the transfer, and it helps secure the transaction against fraud.
After the transaction is digitally signed, it’s broadcast to the network, where it awaits confirmation. This is where things get more technical but also more fascinating. The transaction enters a pool known as the mempool, where unconfirmed transactions are temporarily stored before they are added to a new block.
The Role of Mining and Validators
The process of validating and confirming cryptocurrency transactions depends on the specific blockchain network. In Bitcoin and similar cryptocurrencies, miners perform this role. Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles, and the first one to solve the problem gets to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain. This process is called Proof of Work.
Once a miner successfully adds the block, the included transactions are considered confirmed. The more confirmations a transaction has, the more secure and irreversible it becomes. For example, in the Bitcoin network, a transaction with six confirmations is generally considered final and secure against double-spending.
Other blockchains, like Ethereum 2.0 or Cardano, use Proof of Stake mechanisms. Here, validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. These validators confirm transactions and add them to the blockchain in a more energy-efficient manner than mining.
In both systems, however, the principle remains the same: decentralized participants validate and confirm transactions, ensuring the network remains trustworthy and resistant to manipulation.
Receiving Cryptocurrency: The Simpler Side
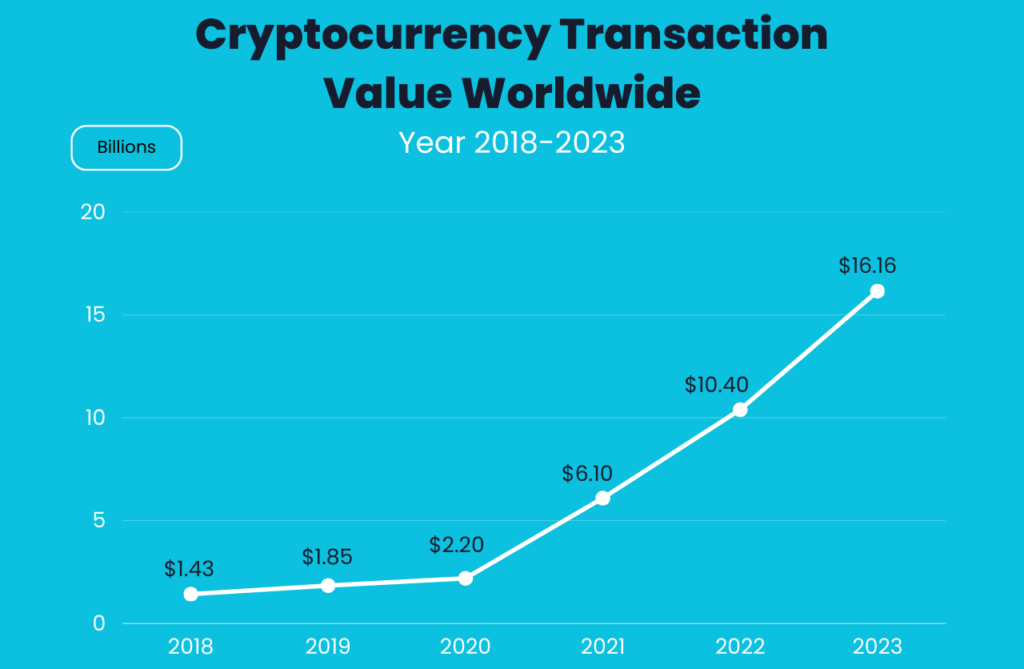
While sending cryptocurrency requires signing transactions and broadcasting them to the network, receiving crypto is much simpler. All you need is your wallet’s public address. This is often presented as a string of letters and numbers, or more conveniently, as a QR code. When someone wants to send you crypto, they use this address to designate the destination.
Once the transaction is initiated and confirmed on the blockchain, the funds will appear in your wallet. The actual process of receiving funds doesn’t require you to be online or take any action—your wallet will automatically detect the transaction and update your balance accordingly.
It’s important to double-check the address you provide to avoid mistakes. Cryptocurrency transactions are irreversible, and sending funds to the wrong address can lead to permanent loss.
Transaction Fees: Why You Pay and How It’s Calculated
One aspect of cryptocurrency transactions that often surprises newcomers is transaction fees. These are small amounts of cryptocurrency paid to incentivize miners or validators to process and include your transaction in the next block. The fee doesn’t go to the recipient or the wallet provider—it goes to those maintaining the network.
Fees vary depending on network congestion and the cryptocurrency being used. During times of high demand, such as market surges or major events, fees can spike significantly. On the flip side, during quiet periods, fees can be minimal. Some wallets allow users to choose their fee level—higher fees typically result in faster confirmations, while lower fees might lead to longer waiting times.
Understanding how fees work can help you plan your transactions strategically, especially if you’re moving large amounts or operating in a business context.
How Long Do Cryptocurrency Transactions Take?
The speed of cryptocurrency transactions depends on several factors, including the blockchain’s design, network congestion, and the fee attached to the transaction. Bitcoin transactions, for example, can take anywhere from 10 minutes to over an hour to confirm, depending on how many confirmations are required and how busy the network is.
Ethereum transactions tend to be faster, often confirming within minutes, although congestion can cause delays. Layer-2 solutions like the Lightning Network or Polygon offer faster and cheaper alternatives for certain types of transactions by handling some activity off-chain before settling on the main blockchain.
Ultimately, choosing the right blockchain and understanding its behavior will help you estimate transaction times and manage your expectations when sending or receiving crypto.
Security and Privacy in Crypto Transactions
One of the core appeals of cryptocurrency is the balance between transparency and privacy. All transactions are recorded on a public blockchain, which means anyone can view the transaction history of a given address. However, the identity of the person behind the address is not publicly disclosed.
That said, blockchain forensics tools can sometimes trace addresses back to individuals, especially if they’ve interacted with centralized exchanges that require identity verification. For those who value privacy, cryptocurrencies like Monero or Zcash offer enhanced anonymity features that obscure sender and recipient addresses as well as transaction amounts.
Always exercise caution when handling private keys and interacting with unknown addresses. Scams, phishing attacks, and malware are common threats in the crypto world. Keeping your keys secure and using trusted platforms is essential to ensuring your funds stay safe.
Smart Contracts and Complex Transactions
Beyond simple transfers of value, cryptocurrency transactions can also involve smart contracts. These are self-executing agreements with the terms directly written into code. When specific conditions are met, the contract triggers a transaction automatically. This enables everything from decentralized finance (DeFi) applications to automated token swaps and NFT transfers.
Smart contracts add complexity but also versatility to how transactions are carried out. Instead of just sending funds to a person, you can interact with decentralized apps (dApps) and protocols, making cryptocurrency a foundation for a new generation of digital services.
Mistakes and Reversals: What Happens When Things Go Wrong?
One of the most important things to understand about cryptocurrency transactions is that they are irreversible. Once a transaction is confirmed, it cannot be canceled or rolled back. This is a double-edged sword: while it prevents fraud and chargebacks, it also means that sending funds to the wrong address, or being tricked by a scammer, can result in permanent loss.
Some wallets and exchanges offer safeguards like address whitelisting, transaction confirmations, and two-factor authentication to reduce the risk of errors. However, the ultimate responsibility lies with the user. Always triple-check recipient addresses, transaction amounts, and the legitimacy of any third parties you’re dealing with.
International Transfers and Global Impact
One of the most transformative aspects of cryptocurrency transactions is their potential to reshape international finance. Traditional cross-border transfers can be slow, expensive, and reliant on intermediary banks. Cryptocurrency bypasses these limitations, allowing users to send funds globally in minutes with minimal fees.
This is especially impactful in regions with limited access to traditional banking. Crypto allows individuals in developing countries to receive remittances, participate in global markets, and store value in ways previously unavailable. For freelancers, entrepreneurs, and migrants, crypto provides a powerful alternative to legacy financial systems.
Regulatory Considerations and Legal Issues
As the popularity of cryptocurrency transactions grows, so does the attention from regulators. Many countries are developing legal frameworks to govern crypto usage, aiming to prevent illegal activities like money laundering and ensure consumer protection.
Depending on where you live, you may be required to report cryptocurrency transactions for tax purposes or follow certain guidelines when sending large amounts. Centralized exchanges often require KYC (Know Your Customer) verification, while decentralized platforms typically do not.
Keeping up to date with local regulations is crucial for compliance and peace of mind. As governments refine their crypto policies, understanding the legal landscape will become as important as understanding the technology itself.
The Future of Cryptocurrency Transactions
Looking ahead, cryptocurrency transactions are poised to become faster, cheaper, and more accessible. Innovations such as layer-2 scaling solutions, cross-chain interoperability, and quantum-resistant cryptography are already on the horizon. These developments aim to make cryptocurrency more efficient and secure for users worldwide.
Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) are also likely to influence the landscape. While they may differ from decentralized cryptocurrencies, CBDCs could help normalize digital payments and introduce millions more people to blockchain-based systems.
The continued integration of crypto with mainstream financial services, retail platforms, and mobile devices will make it easier than ever to send and receive crypto. As adoption grows, understanding the nuances of cryptocurrency transactions will be an essential digital literacy skill.
Embracing the New Financial Frontier
Cryptocurrency transactions represent more than just digital payments—they are a revolutionary way of exchanging value, managing assets, and participating in a decentralized financial ecosystem. By understanding how these transactions work, from initiation and validation to confirmation and security, you can engage with confidence in the growing world of crypto.
Whether you’re transferring funds across borders, paying for goods online, or interacting with smart contracts, the principles behind cryptocurrency transactions remain the same: transparency, decentralization, and cryptographic security. With this foundation, you’re better equipped to explore, invest, and thrive in the digital age.
As cryptocurrency continues to evolve, staying informed and cautious will ensure that your experience with crypto transactions remains smooth, secure, and rewarding. The future of finance is decentralized—and it all begins with understanding how cryptocurrency transactions work.

